
Say you have a common 6-sided die and need to roll it until the sum of your rolls is at least 6. How many times would you need to roll?
If you had a 20-sided die and you need to roll for a sum of at least 20, would that take more rolls or fewer rolls on average?
According to [1], the expected number of rolls of an n-sided dice for the sum of the rolls to be n or more equals
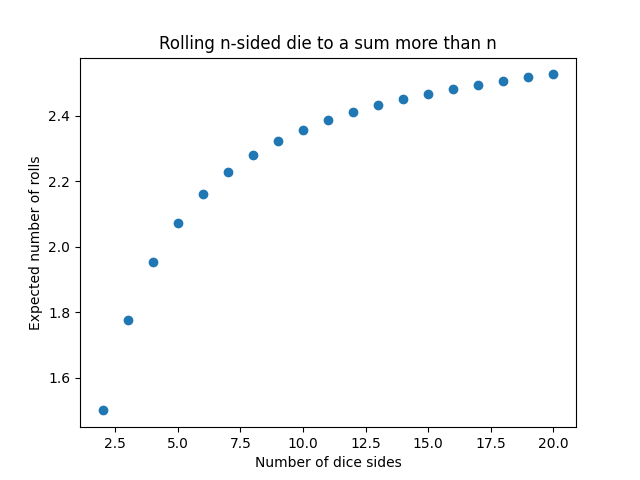
So for a 6-sided die, the expected number of rolls is (7/6)5 = 2.1614.
For a 20-sided die, the expected number of rolls is (21/20)19 = 2.5270.
The expected number of rolls is an increasing function of n, and it converges to e.
Here’s a little simulation script for the result above.
from numpy.random import randint
def game(n):
s = 0
i = 0
while s < n:
s += randint(1, n+1)
i += 1
return i
N = 1_000_000
s = 0
n = 20
for _ in range(N):
s += game(n)
print(s / N)
This produced 2.5273.
[1] Enrique Treviño. Expected Number of Dice Rolls for the Sum to Reach n. American Mathematical Monthly, Vol 127, No. 3 (March 2020), p. 257.

Like my old man used to say,,,”It boggles the mind!” :=)
That … is a really unexpected result!
I’ve seen that or a similar equation used for something else. Can someone explain how/why that equation works
There’s an intuition here. Approximate a die roll from 1 to n by a continuous uniform distribution from 1/2 to n + 1/2. The mean of that uniform distribution is n/2 + 1/2 and the standard deviation is n*sqrt(12). It makes sense that 2 rolls should get you to n, but the distribution has a longer tail on the right–the actual number can’t be less than 1–, hence the expected number of rolls to get to n will be something more than 2.
In the limit of large n, everything scales with n, so the problem is equivalent to asking, How many uniform(0,1) random variables do you have to add up to get a sum of at least 1? This will have a finite limit which we know will be more than 2. It’s not obvious to me that it’s e, but when you say it’s e, that makes sense.
Finally, for small n, the discreteness of the distribution makes it easier to reach the endpoint. For example, for a 20-sided die, reaching a “20” is reaching the top 5% of the distribution, but for a 6-sided die, reaching a “6” is the top 17% of the distribution, which should be easier to attain.
So it’s intuitive that the expected number of rolls increases with n and reaches an asymptote that’s some value higher than 2.